1、掌握类型1、2、3、4 和5 的LSA,及类型7 的LSA 在完全次末节区域的作用。
2、掌握次未节区域(NSSA)和完全次末节区域(NSSA Totally Stub Area)特点。
3、掌握两种区域配置方法。
4、完全次末节区域(Totally NSSA)为CISCO 私有的。
2、掌握次未节区域(NSSA)和完全次末节区域(NSSA Totally Stub Area)特点。
3、掌握两种区域配置方法。
4、完全次末节区域(Totally NSSA)为CISCO 私有的。
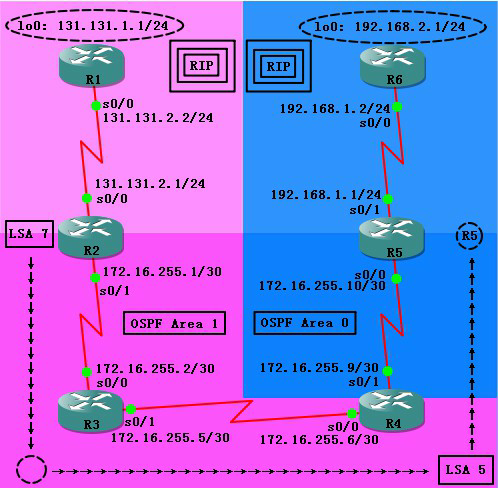
TOP图:
配置好地址信息,测试完互连可达,配置好基本的动态路由协议信息。
在R2和R5上配置路由重分发:
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 10
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#redistribute rip metric 200 subnets
R2(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 10
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#redistribute rip metric 200 subnets
R2(config-router)#exit
R5(config)#router ospf 1
R5(config-router)#re rip me 200 su
R5(config-router)#exit
R5(config)#router rip
R5(config-router)#re ospf 1 me 10
R5(config-router)#exit
R5(config-router)#re rip me 200 su
R5(config-router)#exit
R5(config)#router rip
R5(config-router)#re ospf 1 me 10
R5(config-router)#exit
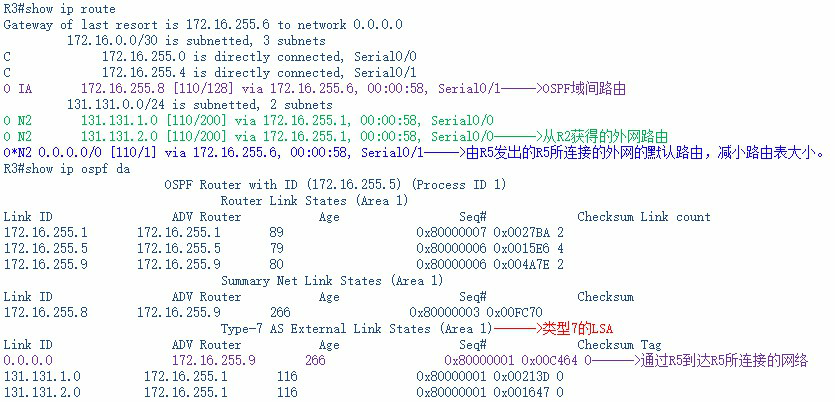
查看R3的路由表和OPSF数据库:

由于area 1 路由违背了stub 区域要求,即stub 区域不能够有ASBR 路由器的特性。因此本实验采用NSSA 的配置方法来减少R3 路由器的路由表大小。
在R4上:
R4(config)#router ospf 1
R4(config-router)#area 1 nssa default-information-originate
R4(config-router)#exit
R4(config-router)#area 1 nssa default-information-originate
R4(config-router)#exit
指出area 1区域为NSSA区域,default-information-originate指明R4向区域1中发送一条默认路由。
在R2和R3上:
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#area 1 nssa
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config-router)#area 1 nssa
R2(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#router ospf 1
R3(config-router)#area 1 nssa
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config-router)#area 1 nssa
R3(config-router)#exit
再次查看R3的路由表和OSPF链路状态数据库:
R2的路由表:
R2#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.255.2 to network 0.0.0.0
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.255.2 to network 0.0.0.0
172.16.0.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 172.16.255.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1
O 172.16.255.4 [110/128] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
O IA 172.16.255.8 [110/192] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 131.131.1.0 [120/1] via 131.131.2.2, 00:00:02, Serial0/0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
O*N2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
C 172.16.255.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1
O 172.16.255.4 [110/128] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
O IA 172.16.255.8 [110/192] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 131.131.1.0 [120/1] via 131.131.2.2, 00:00:02, Serial0/0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
O*N2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 172.16.255.2, 00:09:17, Serial0/1
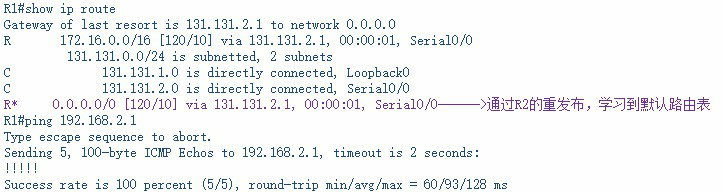
R1的路由表:
为了进一步简化area 1区域的路由器的路由表,可采用完全次末节区域(Totally NSSA)特性来配置area 1。
在NSSA的基础上,在R4上做如下配置即可:
R4(config)#router ospf 1
R4(config-router)#area 1 nssa no-summary
R4(config-router)#exit
R4(config-router)#area 1 nssa no-summary
R4(config-router)#exit
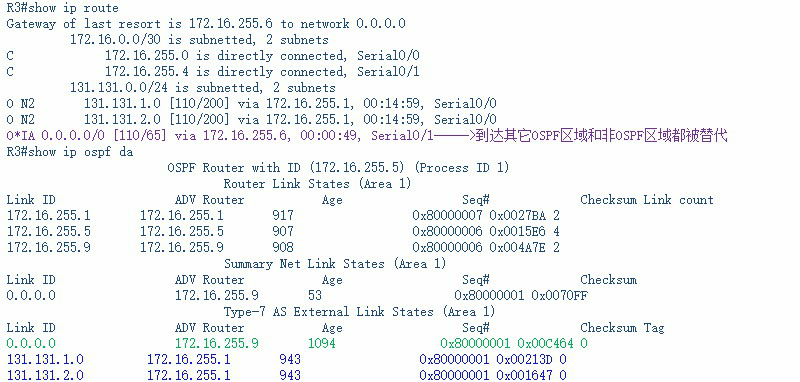
再查看R3上的路由表和OSPF链路状态数据库:
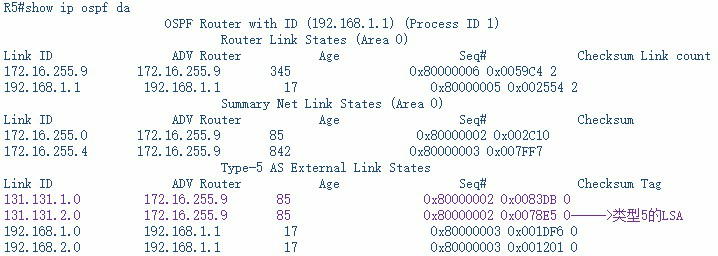
类为完全次末节区域和完全末节区域相似的是:丢弃类型3、4、5的LSA,所以此处把默认路由转发类型7的LSA,以便向R2通告。
从R2收到的类型7的LSA,此类型的LSA到达区域边界路由器(ABR),R4会转化成类型5的LSA向其它OSPF区域通告。
查看R1和R2的路由表:
R1#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 131.131.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0
Gateway of last resort is 131.131.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0
R 172.16.0.0/16 [120/10] via 131.131.2.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 131.131.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/10] via 131.131.2.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 131.131.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/10] via 131.131.2.1, 00:00:17, Serial0/0
R2#show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.255.2 to network 0.0.0.0
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.255.2 to network 0.0.0.0
172.16.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 172.16.255.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1
O 172.16.255.4 [110/128] via 172.16.255.2, 00:26:53, Serial0/1
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 131.131.1.0 [120/1] via 131.131.2.2, 00:00:05, Serial0/0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
O*IA 0.0.0.0/0 [110/129] via 172.16.255.2, 00:12:43, Serial0/1
C 172.16.255.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1
O 172.16.255.4 [110/128] via 172.16.255.2, 00:26:53, Serial0/1
131.131.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
R 131.131.1.0 [120/1] via 131.131.2.2, 00:00:05, Serial0/0
C 131.131.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
O*IA 0.0.0.0/0 [110/129] via 172.16.255.2, 00:12:43, Serial0/1
查看R5上的OSPF 数据库:
由R3发给R4的类型7的LSA在R4发向其它OSPF区域时确实转成了类型5的LSA。
测试连通:
R1#ping 131.131.2.1 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 131.131.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/30/52 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.2 so 131.131.1.1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 131.131.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/30/52 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.2 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/60/92 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.6 so 131.131.1.1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/60/92 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.6 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/75/132 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.10 so 131.131.1.1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/75/132 ms
R1#ping 172.16.255.10 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 92/104/128 ms
R1#ping 192.168.1.2 so 131.131.1.1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.255.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 92/104/128 ms
R1#ping 192.168.1.2 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/99/160 ms
R1#ping 192.168.2.1 so 131.131.1.1
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/99/160 ms
R1#ping 192.168.2.1 so 131.131.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/100/156 ms
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 131.131.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/100/156 ms
一切正常。